Lipid Nanoparticles Encapsulated with siRNA
Nanoparticle-mediated gene therapy has garnered considerable attention over the past two decades. Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) encapsulating siRNA are currently the most extensively clinically validated means of enabling RNA interference. However, determining the precise particle count and the fraction of loaded particles poses challenges. Although, in principle, particles can be counted in cryo-TEM images, the non-uniform distribution of LNPs in vitrified samples on electron microscopy grids makes it difficult to obtain an accurate particle count.
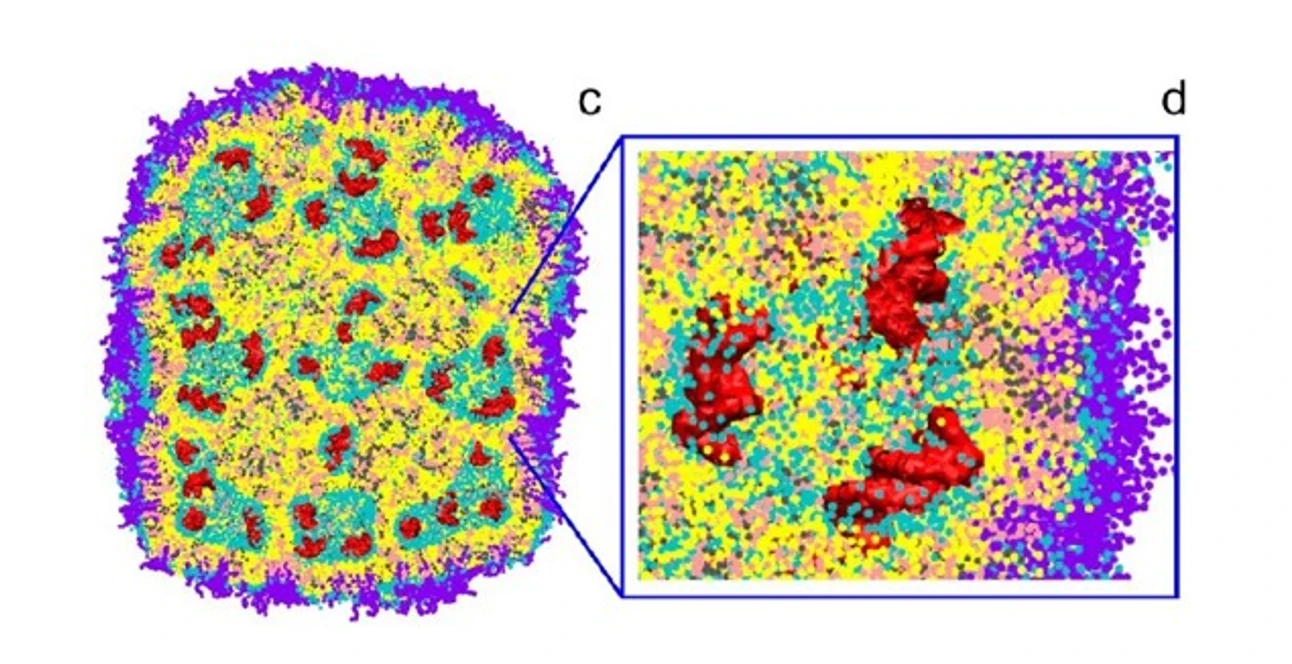
Moreover, the comparable size, shape, and electron density of empty and siRNA-loaded LNPs render cryo-TEM less effective in determining the fraction of siRNA loading. The Flow NanoAnalyzer is used here for quantitative, multi-parameter characterization of siRNA-loaded LNPs. Upon fluorescent staining with SYTO™ 82, the fraction of siRNA loading is determined.
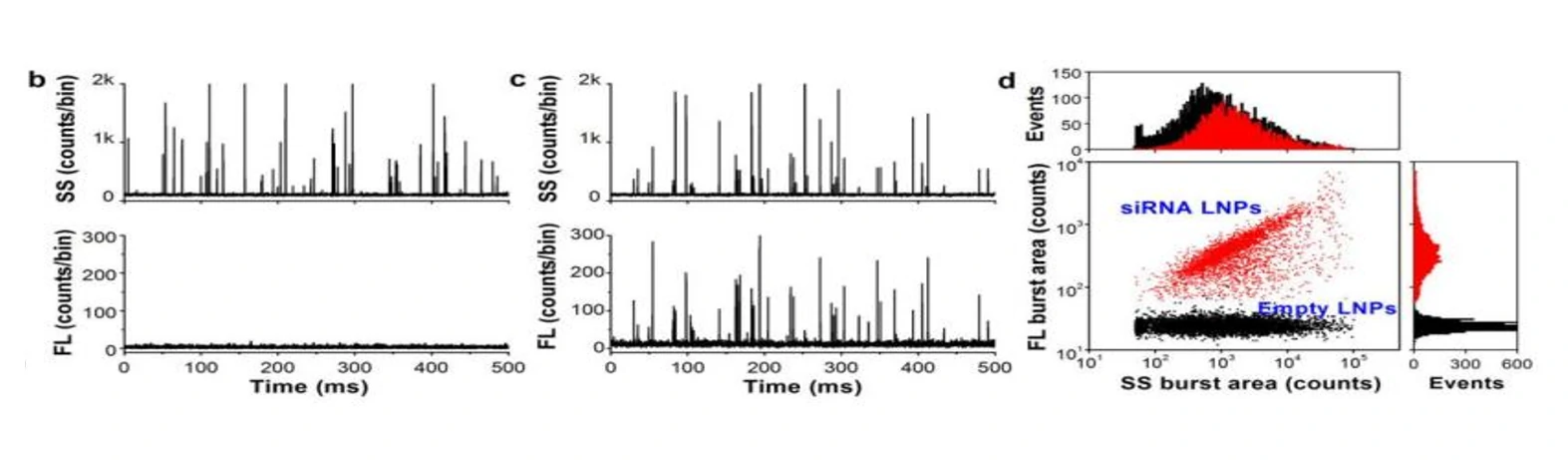
Figure 1. Characterization of siRNA nanomedicine after SYTO™ 82 staining.
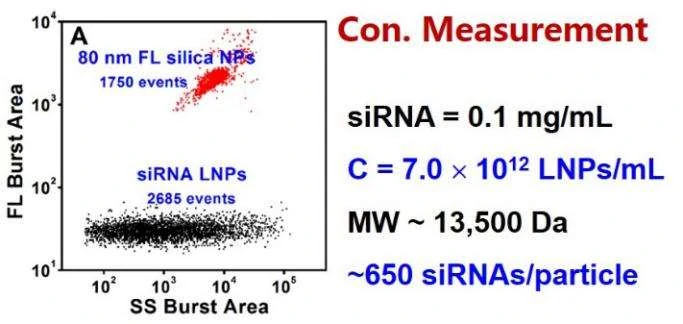
Figure 2. Concentration measurement of unstained siRNA-loaded LNPs by internal standard method.
The Flow NanoAnalyzer is able to detect the side-scatter signal from single nanomedicine particle, and upon SYTO™ 82 staining, empty and siRNA-loaded LNP samples are discriminated, and the fraction of siRNA loading is calculated.
ACS Nano, 2014, 8(10), 10998-11006.





